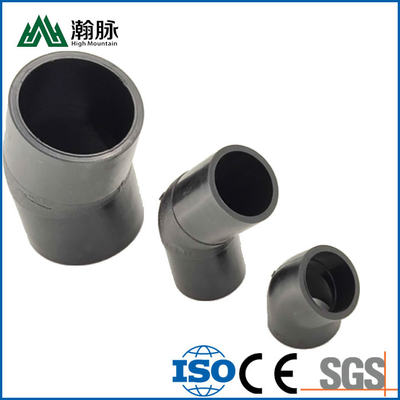
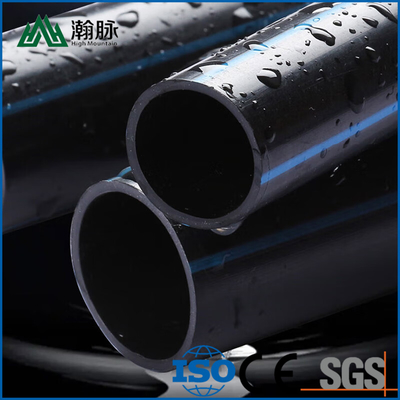
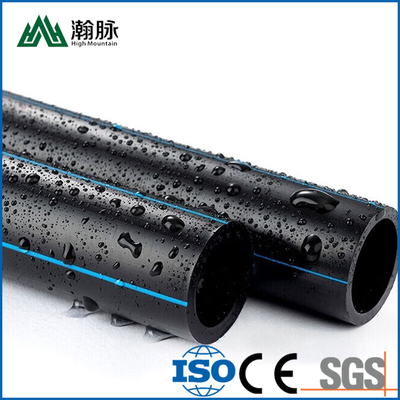
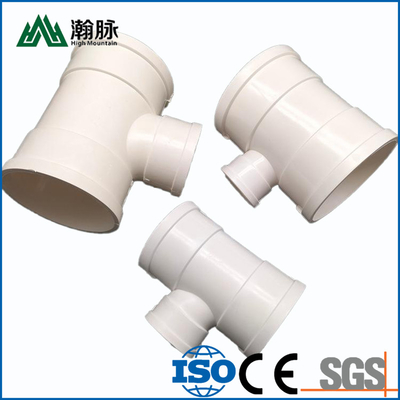
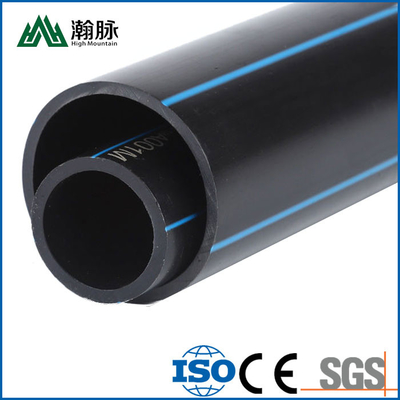
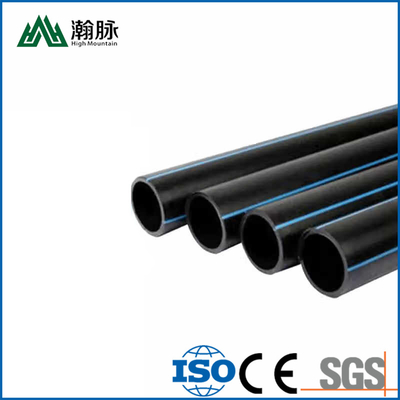
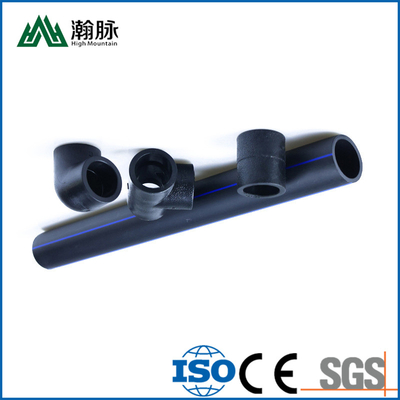
HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe are both made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), but they have different applications. HDPE water supply pipe is typically used for potable water distribution, while HDPE drainage pipe is typically used for sewer and stormwater systems. So, how can you tell the difference between HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe? Here are a few key differences: HDPE water supply pipe is usually thicker than HDPE drainage pipe. This is because it needs to be able to withstand higher pressures. HDPE water supply pipe is typically black, while HDPE drainage pipe is usually white. This is because different colored dyes are used to distinguish between the two types of pipe. HDPE water supply pipe has smooth interior walls, while HDPE drainage pipe has corrugated interior walls. This helps to improve the strength and flexibility of the pipe. If you're not sure which type of HDPE pipe you need, be sure to consult with a professional before making your purchase.

What is HDPE pipe?
HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe are both made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), but they serve different purposes. HDPE water supply pipe is typically used to transport potable water to homes and businesses, while HDPE drainage pipe is usually used to carry wastewater away from a structure.
The main difference between HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe is the application. HDPE water supply pipes are meant for transporting potable (drinking) water, while HDPE drainage pipes are meant for transporting wastewater (water that has been used).
Water supply pipes are typically made of virgin HDPE material, while drainage pipes are often made of recycled HDPE material. Virgin HDPE has no prior history of being used for carrying anything other than water, so it is less likely to leach chemicals into the water it is transporting. Recycled HDPE may have been used for carrying hazardous materials at some point in its life cycle, so it may be more likely to leach contaminants into the water it is now carrying away from a structure.
HDPE water supply pipes are usually solid wall pipes, while HDPE drainage pipes are often corrugated (hollow with ridges on the inside). The solid wall construction of water supply pipes makes them less flexible than drainage pipes, which can be helpful when installing long runs of pipe. However, the ridges on corrugated pipes can help to strengthen the pipe
What are the differences between HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe?
The main difference between HDPE water supply pipe and HDPE drainage pipe is their intended use. HDPE water supply pipes are designed for transporting potable water, while HDPE drainage pipes are meant for transporting wastewater. Both types of pipe are made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), but HDPE water supply pipes have a higher level of purity than HDPE drainage pipes. This means that HDPE water supply pipes are safe for human contact, while HDPE drainage pipes should not be used for drinking water.
HDPE water supply pipes are made to strict standards that ensure they will not leach chemicals into the water they carry. This makes them ideal for carrying potable water to homes and businesses. HDPE drainage pipes, on the other hand, are not held to the same standards because they are not meant to come into contact with humans. As a result, these pipes may leach chemicals into the wastewater they carry, which can be dangerous to people and the environment.
How to install HDPE pipe?
Installing HDPE pipe is a relatively simple process that can be completed by anyone with basic plumbing knowledge. There are only a few steps involved in the installation process, and no special tools or equipment is required. Here is a step-by-step guide to installing HDPE pipe:
1.Measure the area where the pipe will be installed and mark out the route for the pipe.
2.Dig a trench along the marked route, making sure that it is wide enough to accommodate the HDPE pipe.
3.Lay the HDPE pipe in the trench and secure it in place with clamps or straps.
4.Cover the pipe with soil or gravel and compact it around the pipe to form a tight seal.
5.Test the HDPE pipe by performing a pressure test or watertightness test.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!